Video on Demand or VoD Streaming, as the term suggests is a way of streaming video content from a platform as and when the viewer wants to. It essentially puts power back in the hands of the viewers instead of the broadcasters, as used to be the case in the early days of media and even during the first forms of online streaming.
When you click a YouTube video embedded on a website or watch a movie on Netflix you are experiencing VoD streaming. As long as the video is hosted on these platforms and you can access them, all you have to do is click play.
It is no surprise that more consumers are turning to VoD streaming for their video consumption needs. According to Statista, the number of users in the VoD segment of the market is expected to rise to almost 3 million by 2026.
How Does VoD Work?
VoD streaming falls under the category of over-the-top (OTT) streaming, which encompasses the streaming of all types of content – video, audio and VoIP calling – over the internet.
Unlike traditional media broadcast and content distribution, this type of streaming circumvents cable and telecom networks and goes directly from the content creator or distributor directly to the end user or viewer.
Providers of VoD first organize their content into video libraries. They then open up access to these libraries that viewers can make use of in different ways based on the model chosen by the business. The viewer chooses the video content they want and clicks play. In the case of VoD, the source of the video content are static files (as opposed to a feed from a camera in the case of live streaming). The video files are broken up into smaller pieces according to standardized rules and methods called video streaming protocols. These pieces are delivered to the end user for reassembling and viewing.
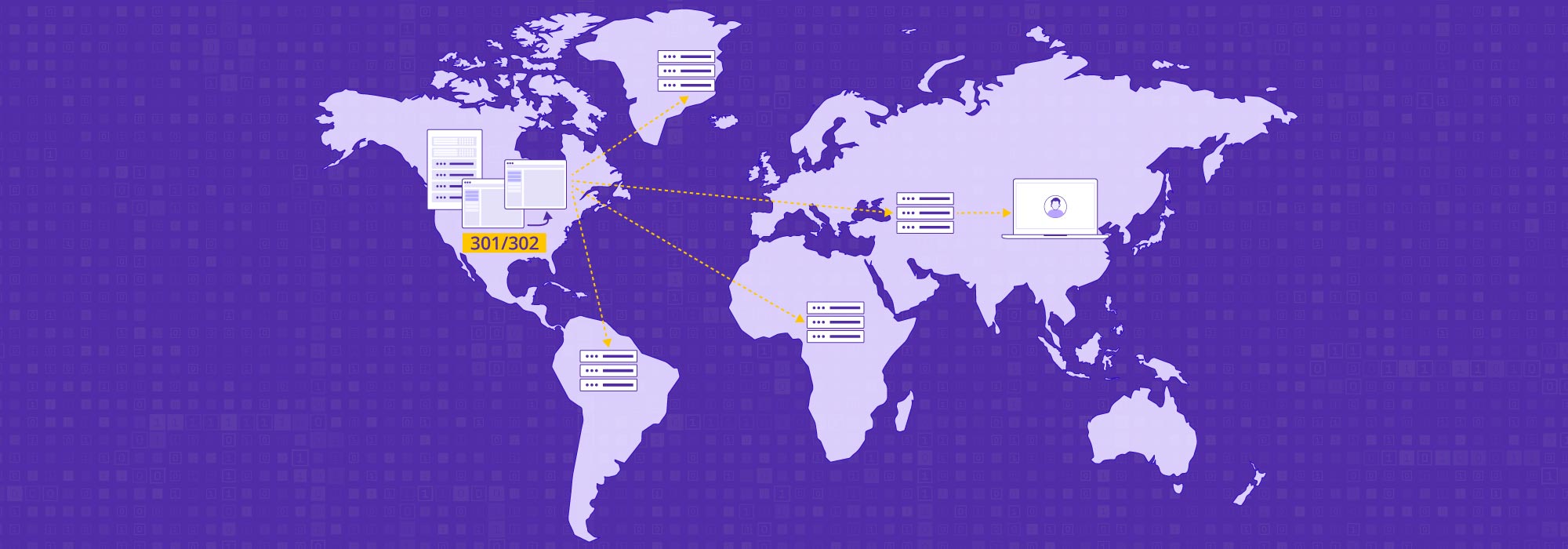
Viewers can watch the VoD content from any location at any time. To ensure that the viewing experience is consistent for consumers distributed across the world, sometimes businesses also use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) for video streaming. This is a network of servers and data centers spread around the globe that brings the content closer to the end users.
VoD vs Live Streaming, What’s the Difference?
The main difference between VoD and Live Streaming comes down to how the content to be streamed is accessed. In VoD streaming, the content is accessed from libraries of previously recorded and stored files, while in live streaming, the content is accessed and consumed in real time. To use a very simple example, the live broadcast of a major sporting event, say the UEFA Champions League final, can be live streamed by authorized sources, such as the Facebook page of the host country’s top sports channel. Now the highlights of the same match, or even the full replay, can be recorded and saved as a video file on their YouTube channel for fans to view later if they missed the live event.
Note that both VoD and Live Streaming are forms of video streaming and the viewer does not have to download the original files. Both operate based on how video streaming works – by breaking down the video file into small packets of data, each of which will be interpreted and played on the viewers device on the go.
What are the Advantages of Video on Demand Streaming?
With more consumers taking to streaming as a means of viewing their content, businesses also have new opportunities to capture their attention and grow an audience that can be monetized eventually. The choice of platforms, formats and monetization models comes down to the creators’ preferences and individual cases but there are some clear advantages to choosing VoD streaming.
Convenience
From a consumer’s point of view, the biggest advantage of VoD Streaming is the convenience it provides them. They can view the content as and when they like, from the comfort of their homes.
Similarly, creators and businesses can also take advantage of VoD Streaming to keep viewers engaged with their content even if they cannot catch the live streams.
Wide Variety of Content
Closely tied to the benefit of convenience is the wide variety of content that users can access on demand. For example, if they are unable to catch a live stream or not completely satisfied with how the live stream was covered, they can explore different versions of replays and highlights of the same event, on demand if they are available from other sources.
On the other hand, creators benefit from having the freedom to exercise their creativity and vision in their videos without having to comply with advertisers’ guidelines or restrictions imposed by the real-time nature of live streaming. For example, if a creator wants to add their own opinions and views to specific sections of the match footage, they can insert them, add graphics and make other edits before releasing the video for streaming on demand.
Cost – Lower and Flexible Subscription Fees
VoD streaming services also cost less for the consumer, in comparison to traditional methods of video consumption such as cable. It also does away with the added costs of equipment rental and other hidden fees. Cable subscription can cost users up to over $2000 a year, more than 10 times the yearly cost of subscription plans associated with VoD platforms.
Most plans also come with the flexibility of monthly payments and the option to cancel the subscription any time. Instead of purchasing entire bundles which may also include programming that viewers don’t need, VoD streaming allows them more control to pick and choose what they want from a catalog.
This also benefits businesses indirectly since they can rely on recurring revenue from viewers who genuinely want to engage with their content.
Availability across Different Devices
Streaming video content on demand also gives viewers the convenience of watching across their many devices. As long as they have an internet connection, they can access the video on their laptops, phones, tablets and even smart TVs. Some VoD streaming services like Netflix also come with the option of directly broadcasting to a smart TV through a browser.
The Different Monetization Models for Video on Demand Streaming
Businesses producing video for streaming on demand do have to monetize their content at the end of the day. The very nature of VoD streaming opens up a few different models on how they can accomplish this.
Subscription Video on Demand (SVoD)
Perhaps the most common form of monetization, Subscription Video on Demand allows creators to be paid by their viewers on a recurring basis. This could be through a weekly, monthly or annual fee which allows viewers access to the creators’ video libraries and watch videos at their convenience, with no ads or pop ups to interfere with their experience.
The big streaming giants Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+ and Hulu and others of a similar nature operate on this SVoD model. This model of monetization is usually adopted by businesses with large video libraries.
Ad-Based Video on Demand (AVoD)
Another way that creators can monetize their VoD content is through advertising. This model works on the basis of allowing viewers to stream the video content for free but at the cost of having to watch ads that are allowed by the creator. The ads are what earn revenue for the business, and these can appear at the beginning of the video (Pre-roll), in the middle (Mid-roll) or at the very end (Post-roll).
Since the revenue is usually proportional to the number of times the ads are seen or clicked, this type of model is usually adopted by creators with a large viewership or audience base. Some common video platforms that allow the AVoD model of monetization are YouTube and Daily Motion.
Transaction Video on Demand (TVoD)
A third model for monetizing VoD streaming is through a per-view basis. In this model, customers pay to access individual content assets in one-time transactions instead of the entire library, like checking out items off a shopping cart. For example, Amazon Prime offers the option of purchasing individual movies, episodes of TV shows or specific seasons. Think of it as renting a much anticipated movie like in the 90s but digitally. The TVoD model is best suited for when the videos are highly popular but the whole library is not too big. The access to the content through the TVoD model could be permanent or DTR (Download to Rent) in which case the content will be available for a specific period of time for a smaller fee. Other platforms that use the TVoD model are Google Play and iTunes.
For businesses intending to take advantage of the popularity of VoD streaming and the benefits it provides, CDNetworks offers a Media Delivery solution that delivers high quality VoD content anywhere and on any device, along with live broadcast. It pulls content directly from the customer’s origin server or CDNetworks Cloud Storage and provides a host of benefits including bandwidth scalability, reduced traffic congestion and cost without compromising video stream performance. To explore these benefits and plenty more for your VoD needs, choose a free trial of Media Acceleration – VoD today.