Live streaming has become a central tool for businesses to reach a wide audience, grow their networks, and ultimately increase exposure.
Buffering, poor audio, and pixelated content are just a few examples of issues associated with live streaming. We’re going to look at a number of ways you can circumvent these problems and deliver your audience with the best viewing experience possible.
The Importance of Live Streaming Quality
Many variables can affect the quality of your stream, from the equipment you use to the strength of your internet connection.
Having a poor quality live stream is one way to lose viewers. Given the abundance of both live streaming and video-on-demand content available nowadays there will be many better options for your audience should they look elsewhere for higher quality streams.
What’s more, if you depend on live streaming as a monetization channel, then research has shown that poor streaming quality will directly impact your revenue.
At CDNetworks, we offer solutions for real-time streaming and interactive viewing experiences for global users. Our high-speed, low-latency streaming works across various devices.
Drawing on our expertise, we have created this best practice guide to help you achieve a perfect, uninterrupted video stream.
Key Factors Influencing Live Streaming Quality
When it comes to live streaming, it’s essential to understand the various factors that can impact quality and affect both viewer experience and revenue potential.
Anything from poor network speed and lack of internet access to unsuitable encoder settings and the device used for live streaming can impact video quality. Understanding these fundamental factors is crucial to avoid common mistakes and effectively utilize available technology.
Network Speed
Network speed is perhaps the most significant factor affecting video quality. With a fast network, you can live stream with low latency and maintain high image quality.
Network speed is crucial for the viewer’s live stream experience. An intermittent connection can cause the stream to freeze, buffer, pixelate, or disconnect, leading to a poor viewing experience and ultimately driving viewers away.
Location
While access to good internet is improving, it still varies greatly from region to region, and where you’re broadcasting from will affect the quality of your live stream. Also, whether your viewer is in close proximity to a media server of your chosen streaming platform will impact their streaming capabilities.
Encoder settings
Encoding and transcoding are other key aspects of live streaming, and the encoder settings that you select will directly impact the quality of your stream. When choosing encoder settings, it’s essential to factor in your upload speeds and your audience’s download speeds.
Choosing unsuitable settings for the given equipment and internet speed will result in buffering or low-quality streams for your viewers. We will discuss the optimization of encoder settings in a little more detail later.
Device
Streaming quality heavily depends on the device you use for recording and broadcasting. A lower-quality recording device will naturally result in a lower-quality stream.
Whether you use a smartphone, laptop, desktop, or dedicated streaming hardware, it’s essential to be familiar with the device and its technical requirements before starting the live stream.
A device with a high-quality camera and audio, powerful processing capabilities, and robust connectivity options can significantly enhance your live stream.
Read More:
Essential Tips for High-Quality Live Streaming
Here’s our expert guide to achieving high-quality, effective live video streams. Avoid pixelated content and broken audio by following these key steps: ensure proper hardware and software setup, maintain a strong Wi-Fi connection, implement network optimization, and, most importantly, conduct a practice run before going live.
Following these steps will save you time and effort, help your live stream run smoothly, and ensure good audience engagement.
Check Your Internet Speed
Before starting your live stream, the first step is to perform an internet speed test, which can be easily done online. The required internet speed will depend on the quality you aim to broadcast.
The higher the desired quality, the higher the internet speed required.
Use a Reliable Internet Service Provider
Speeds will differ depending on your internet provider. Therefore, it’s worth taking the time to research which provider would be best for your region and your requirements.
If you’re concerned about an unstable wireless connection, use an Ethernet cable to connect your router directly to your device for a more reliable and faster connection.
Invest in High-Quality Equipment
Cutting corners on your equipment may save you money in the short term, but it’s also likely to negatively impact how your business is viewed.
Investing in high-quality camera and audio equipment may set you back initially, but the benefits will be obvious when you can deliver beautiful, sharp images and crisp, professional sound to your audience.
High-end equipment is only worthwhile if you’re using it to the best of its abilities. Your lighting and acoustics are hugely important, and paying attention to these could take a lower-quality camera, webcam, or microphone to the next level.
Do a Trial Run
Given the number of variables at play, testing your stream is vital and allows you to identify any major issues before broadcasting live.
It’s advisable to test your broadcast on both slow and fast connections to see how your stream fares on each, while it’s also wise to test how your equipment copes under intense workloads.
For example, you want your camera, audio equipment, and encoder to all be able to perform well under stress to ensure a reliable live stream.
Optimize Your Encoder Settings
There are specific ways of optimizing your chosen encoder settings in order to deliver the best possible stream.
If possible, you should try to ascertain where the majority of your audience is viewing from and the strength of their connections. That way, you’re able to optimize settings for aspects such as video resolution, frame rate, codec, and video bitrate.
Use Optimal Bitrate for Streaming
If your bitrate is set too low, the file will be compressed too much, and viewers will be unable to view it in high resolution. Conversely, if you attempt to stream at too high a bitrate, it is likely that your viewers will not have the capability to process all of the data, degrading the quality of the stream.
Full HD 1080p video at 60fps usually requires a bitrate of between 3.5 and 6 Mbps, whereas 720p requires less, usually between 2.5 and 4 Mbps. Having said that, individual platforms have different guidelines for streaming with regards to bitrates and fps.
Typically, the recommended audio bitrate is around 128 Kbps, much lower than that of video.
One of the main factors affecting bitrate are the streamer’s internet upload speed and the capacity of the chosen encoder. The better your upload speed, the higher the bitrate you’re able to operate at without causing issues such as frame drop.
Sourcing out the best internet provider available for your area is an accessible way of optimizing your bitrate speeds. Meanwhile, lower-quality encoding software is unable to process videos of a higher bitrate as efficiently as specialized hardware encoders can. If your budget allows, investing in high-end encoding hardware is another way to optimize your bitrate speed.
How to Optimize Your Stream Quality with CDNetworks
Live streaming requires a robust and optimized infrastructure to ensure high-quality video and seamless viewing experiences. At CDNetworks, we specialize in enhancing video quality and efficient content distribution. Our solutions maximize compatibility, minimize latency, and provide secure, reliable streaming. Here’s how CDNetworks achieves this…
How CDNetworks Optimizes Video Quality
To maximize compatibility with various network environments and playback screen sizes, CDNetworks converts the live stream, including transcoding into adaptive bitrates and different resolutions.
Our media processing systems optimize video quality and provide high definition by leveraging our Low Bandwidth High Definition technology. This approach helps save bandwidth costs while maintaining high resolution.
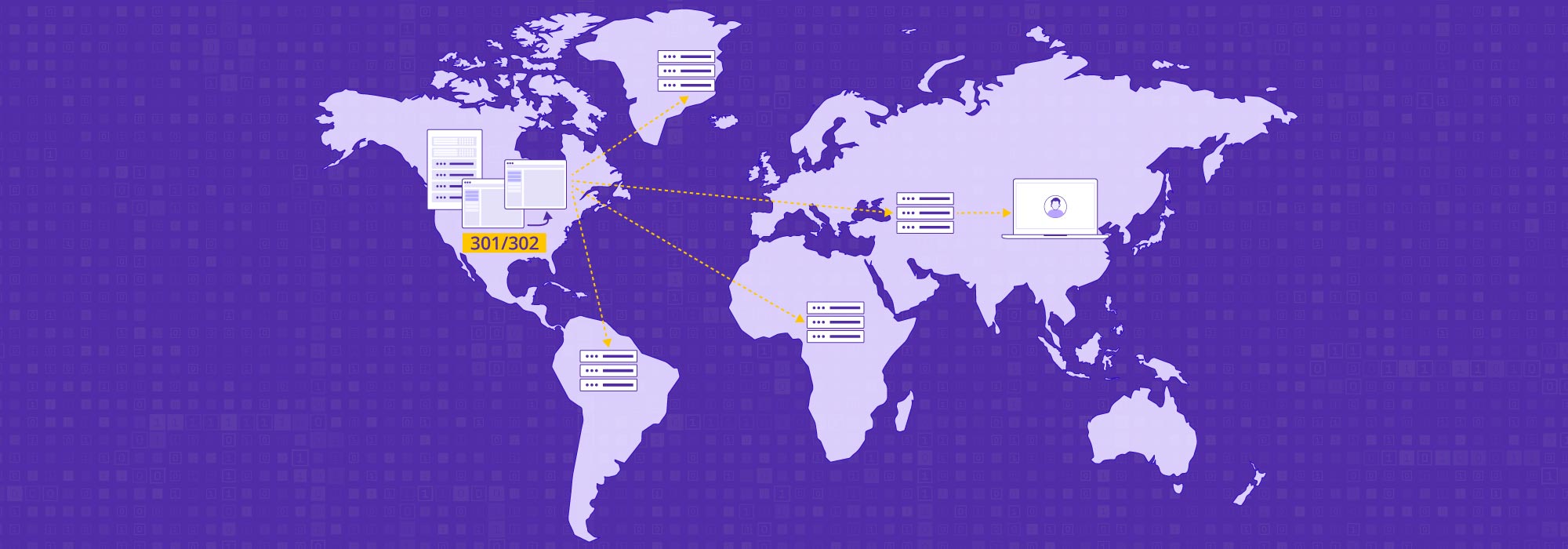
Content Distribution
For distribution, a global content delivery network (CDN) efficiently distributes the content to viewers worldwide. CDNetworks ensures the content is delivered from the server closest to the audience for fast delivery, optimizing the live stream for all devices and networks to provide an optimal viewing experience without latency or stuttering, even during high viewership.
Our solutions
Media Acceleration Live Broadcast
An independently developed service offering a stable, fast, and secure end-to-end live streaming experience. Employing multiple advanced technologies such as Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB) and private streaming media transfer protocol, the service provides one-stop solutions for video ingestion, processing, delivering, and decoding. It renders a fast, stable, and secure live streaming acceleration service and provides users with an excellent experience of low-latency, buffer-free viewing.
Cloud Live
A user-friendly and all-in-one live streaming platform ideal for enterprise-level conferences, online educational courses, and sporting events. You can share live content directly with your global audiences at any scale using our cloud-based platform.